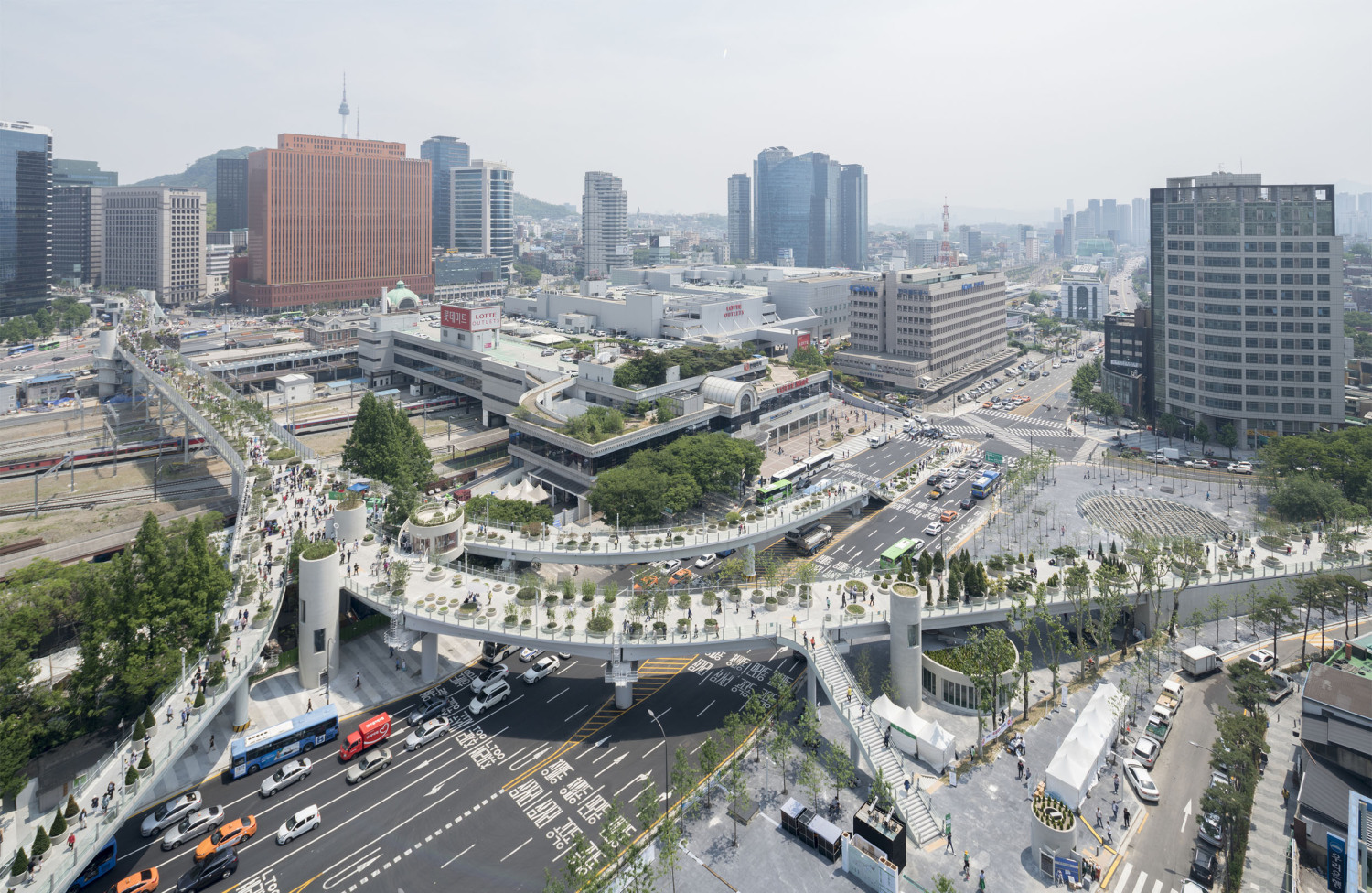
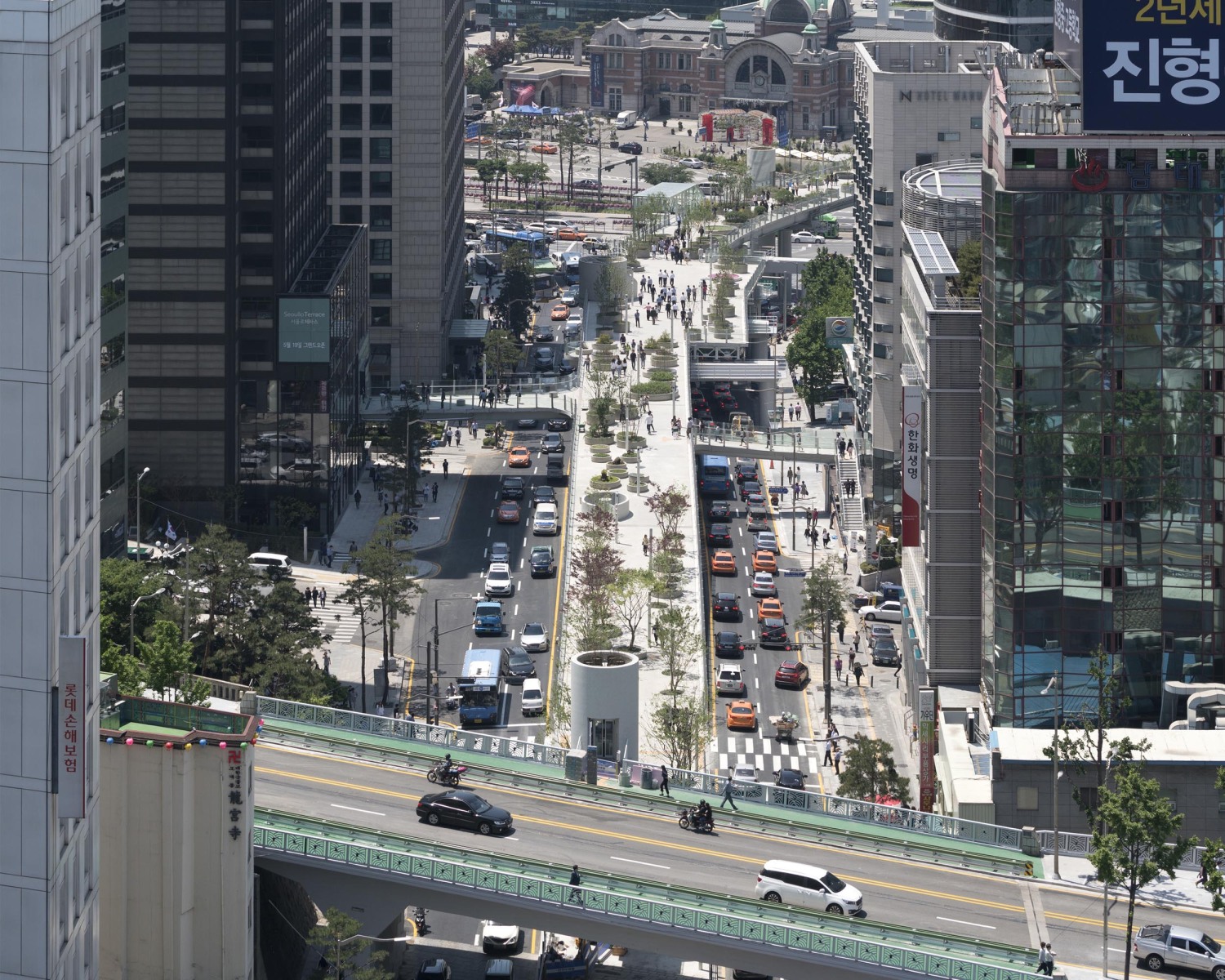
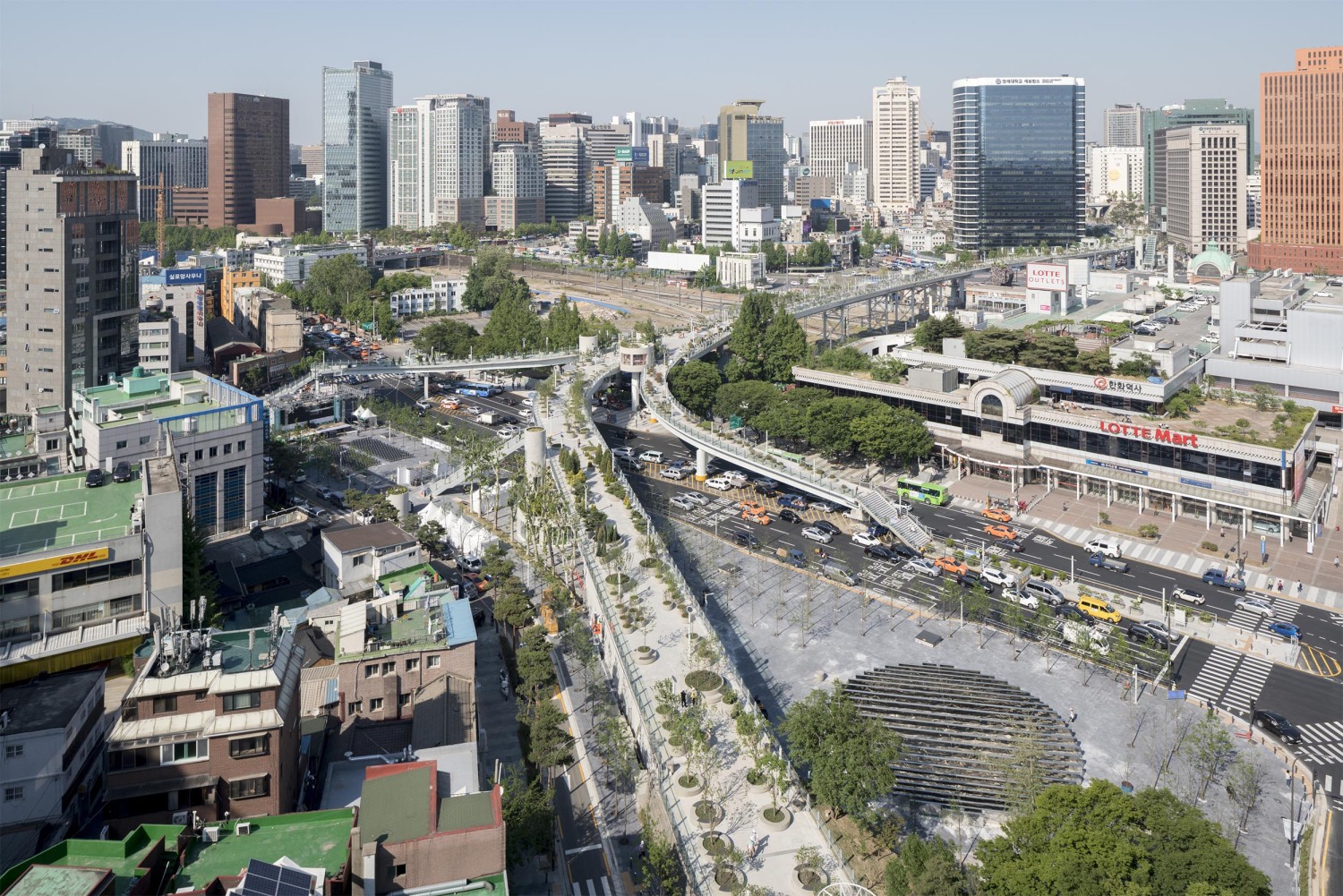
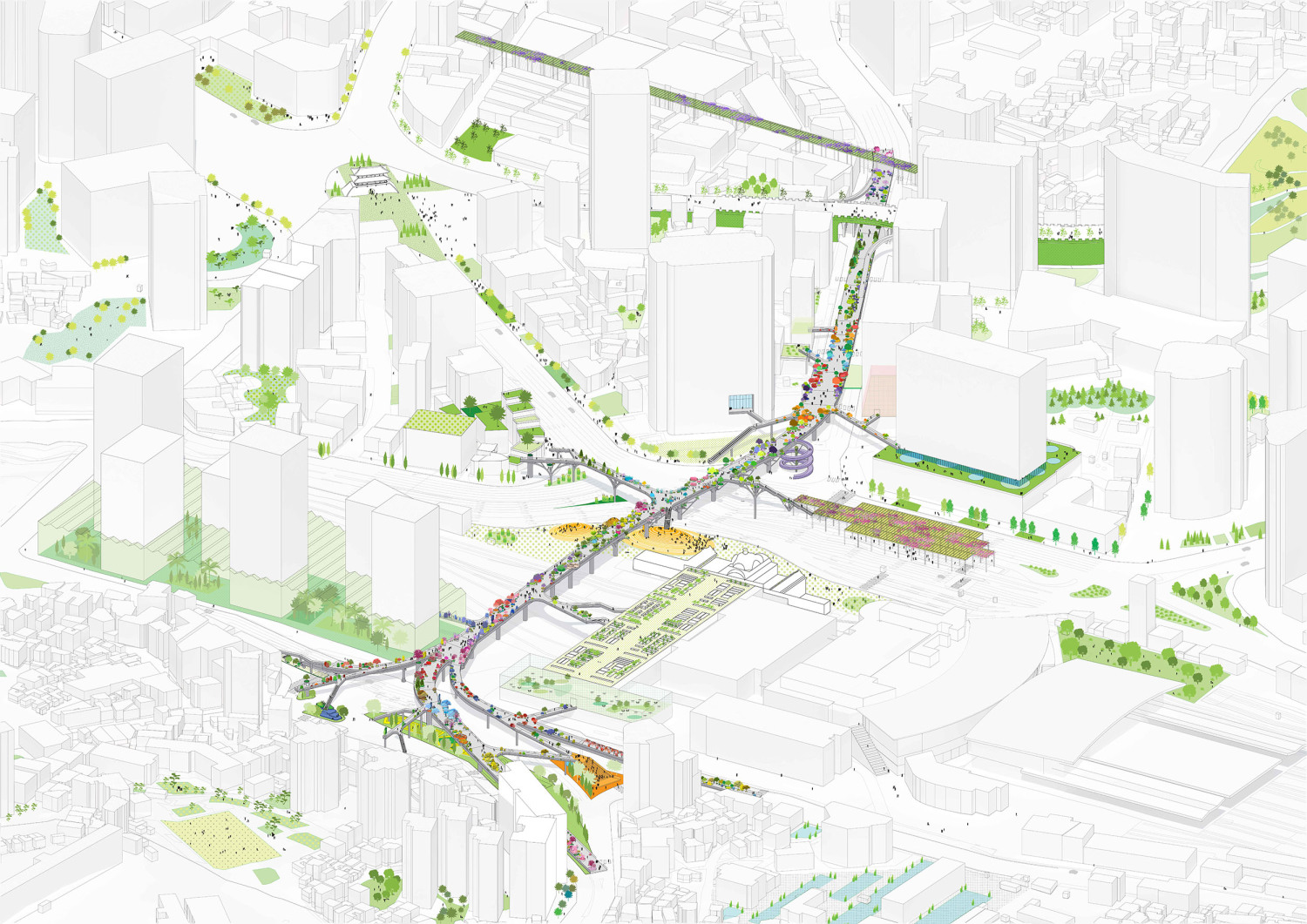
首尔市交桥建于20世纪70年代,旨在为南大门市场(Namdaemun market)提供车辆通道,南大门市场是首尔东部最大的传统市场,横跨车站区域,通往西部的各个公园。经过2006年严格的安全检查,首尔市政府认为这座17米高的立交桥结构不安全,打算拆除重建,并在2009年禁止重型车辆进入高架桥。经过与居民和专家的进一步协商,该项目于2015年启动设计竞赛,计划将总面积为9.661平方米的立交桥改造为人行步道和公共空间。
The Seoul Station Overpass was built in the 1970s to provide a vehicular connection from Namdaemun market, the largest traditional market in Seoul to the East, across the station area to the various parks in the West. Following intensive safety inspections in 2006, the City of Seoul deemed the 17-metre high structure of the overpass unsafe and intended to demolish and rebuild it, banning heavy vehicles’ access to the elevated roadway in 2009. Further consultation with residents and experts lead to the plan to regenerate the overpass, which totals 9.661 m2 in area, into a pedestrian walkway and public space, with the design competition launched in 2015.
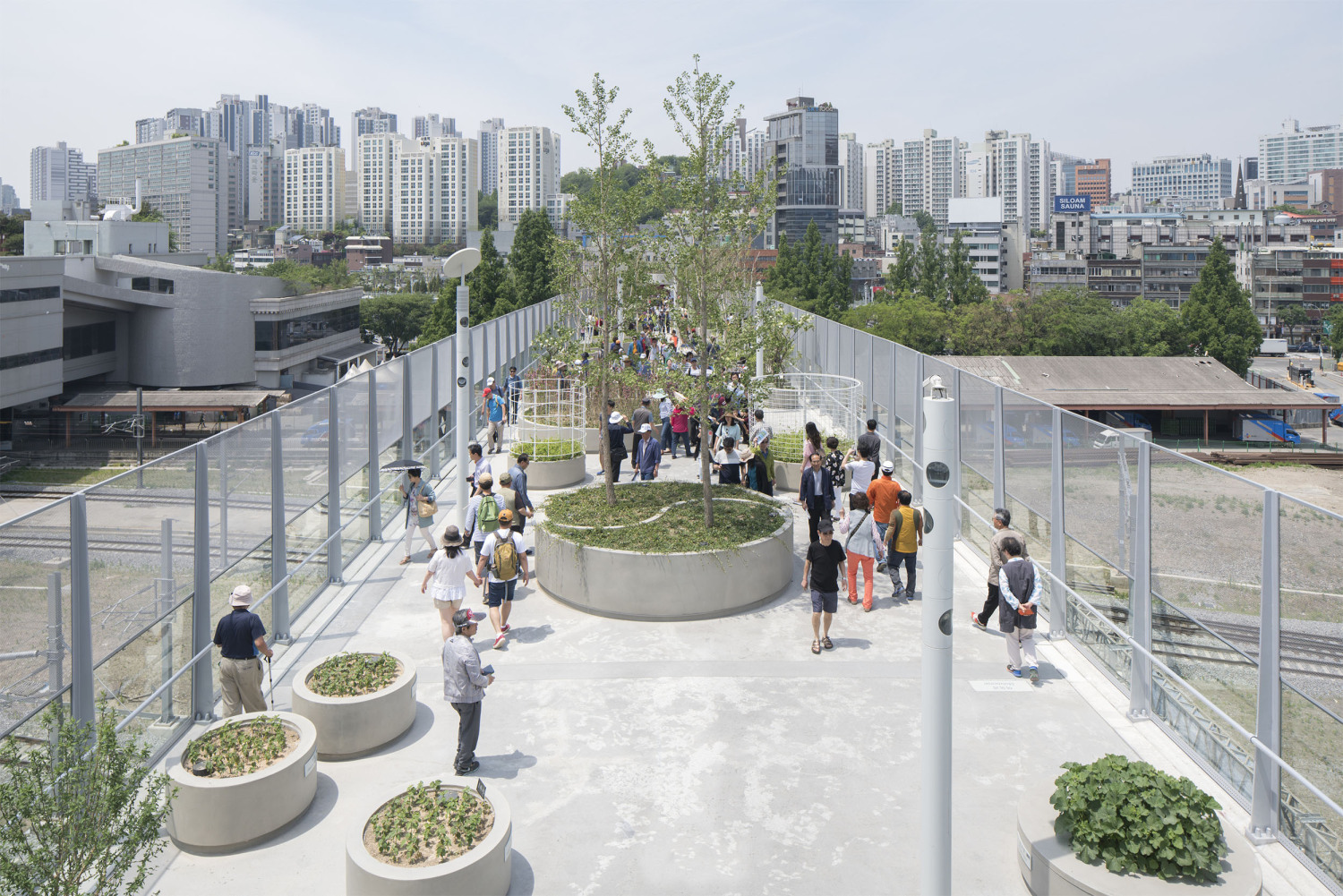
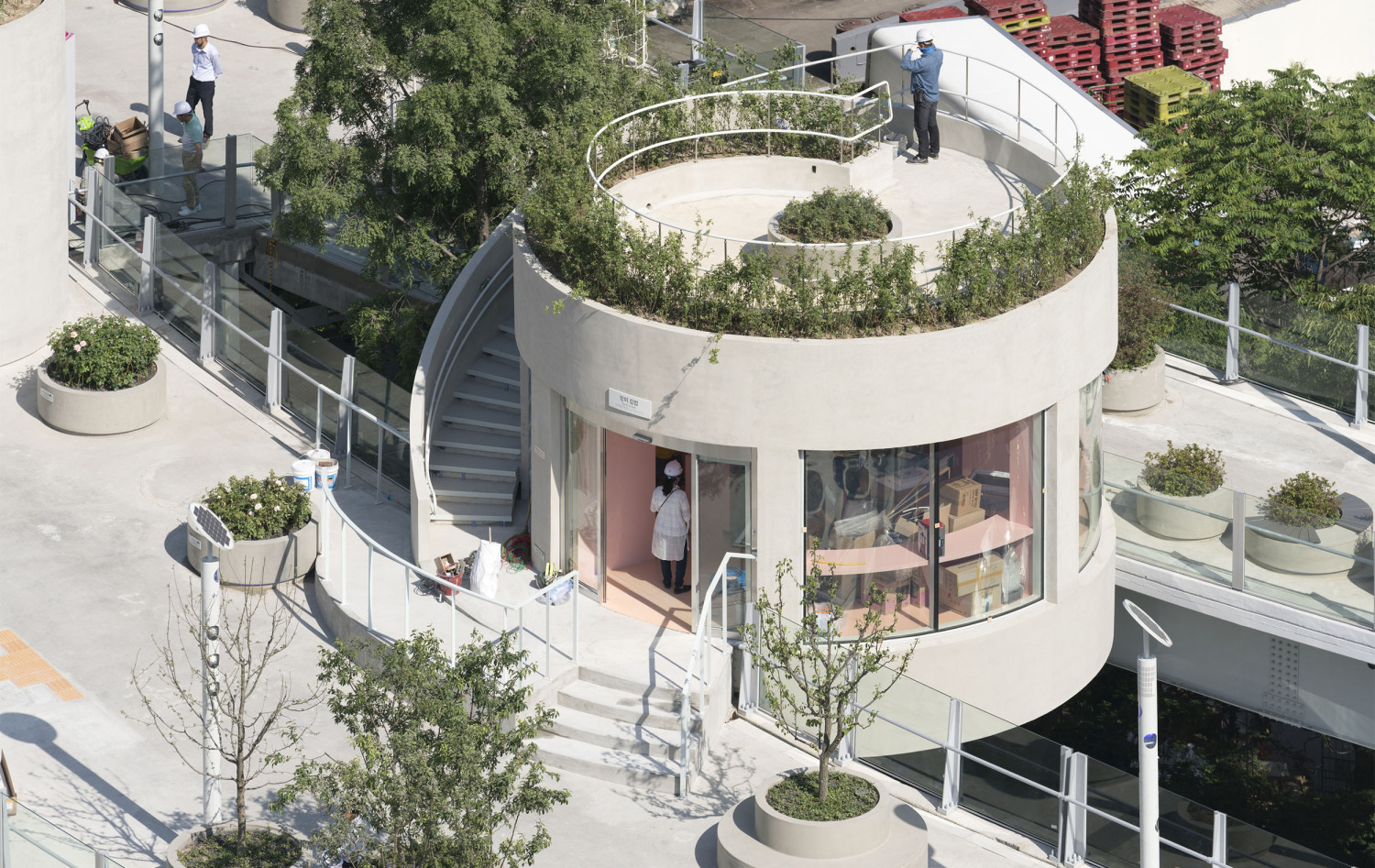
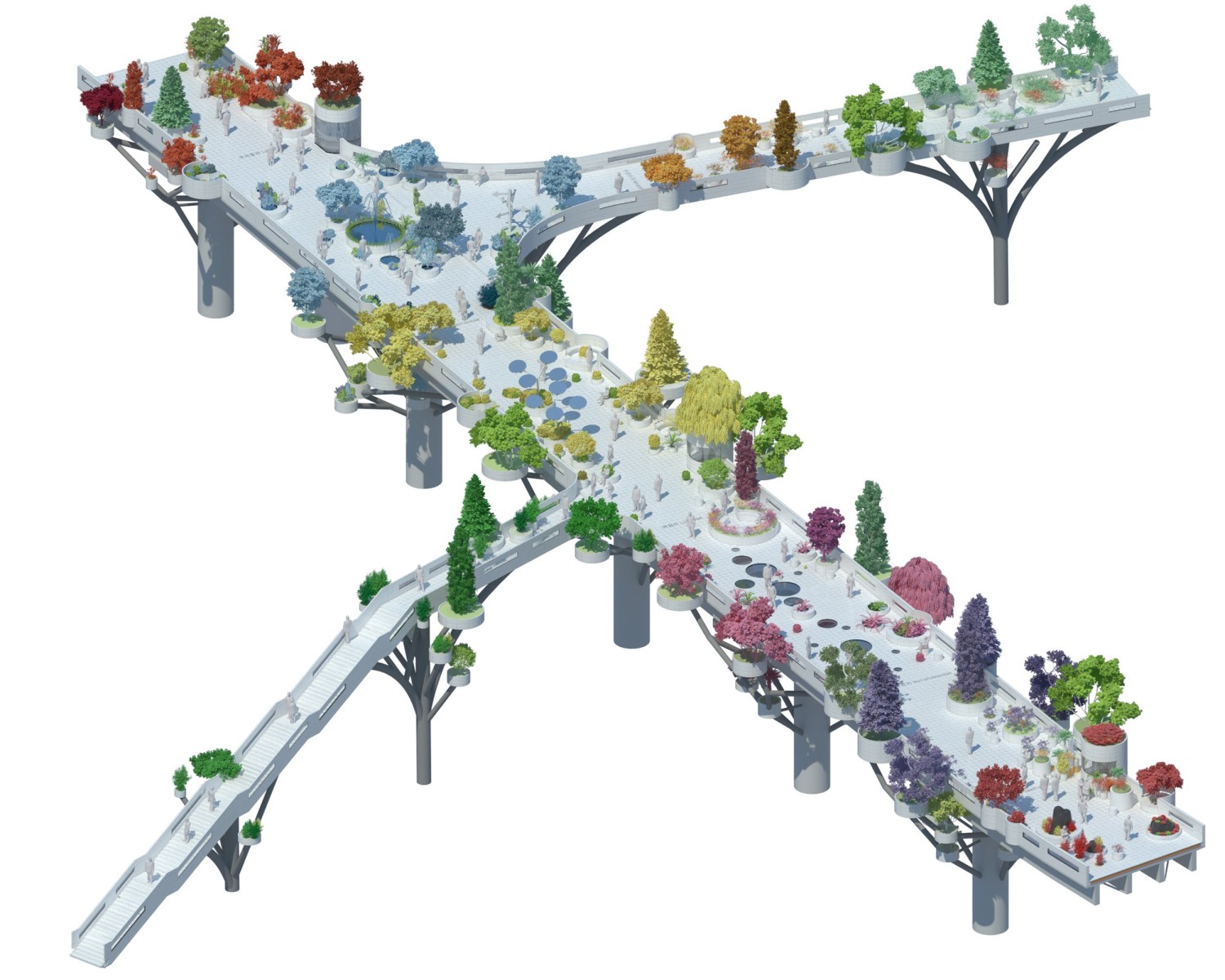
亚洲城市的许多高架桥和人行天桥都是纯粹的交通空间,但由于首尔立交桥并不仅仅是为车辆交通而建,因此就有机会在首尔市中心创造一个独特的公共空间。在引入新的休闲功能的同时,要使这个空间尽可能的绿色化,需要一种模块化和适应性的方法。MVRDV的设计创造了一个植物图书馆,一个韩国植物园的物种种植在“邻近地区”,并沿着938米长的车站立交桥按照韩国字母的名字排列,除了不同大小的圆形花盆外,项目还设计了许多丰富的空间,如茶室、花店、街头市场、图书馆和温室,将提供丰富的元素,使首尔空中花园充满活力
Many viaducts and pedestrian overpasses in Asian cities are purely functional elements, but due to the scale of the Seoul Station Overpass which was built for vehicle traffic, an opportunity exists to create a unique public space in the heart of Seoul. The ambition to make this space as green as possible while introducing new leisure functions requires a modular and adaptable approach. MVRDV’s design creates a library of local plants, a Korean arboretum of species planted in ‘neighbourhoods’ and arranged along the 938 metre length of the Station Overpass according to their names in the Korean alphabet. In addition to the circular plant pots of varying sizes, a series of customizable activators such as tea cafés, flower shops, street markets, libraries and greenhouses will provide a catalogue of elements which will enliven the Seoul Skygarden.
未来,立交桥将会种植新的植物,从而成为一个“城市苗圃”,为周边地区提供苗木。楼梯、电梯和自动扶梯以及新的“卫星”花园的附加结构可以连接到空中花园,就像从现有的结构墩上长出的树枝一样。这些扩展可以激发该地区的绿化和公共空间的进一步增加,并将通过与每个社区相关的植物物种将天空花园与周围环境连接起来。
In the future, the overpass will evolve with new plants and new activators so as to become an ‘urban nursery’, rearing trees for the surrounding districts. Additional structures of stairs, lifts and escalators as well as new ‘satellite’ gardens, can connect to the Skygarden, sprouting like branches from the existing structural piers. These extensions can inspire further additions to the area’s greenery and public spaces, and will connect the Skygarden to its surroundings both physically and visually through plant species related to each of the neighbourhoods.
这些街区由于其字母顺序和一致的标识,以及每个集群中植物物种之间的明显区别,使得“空中花园”更有标志性,并赋予了每个空间独特的特征。
These neighbourhoods make the Skygarden easy to navigate due to their alphabetical order and consistent signage, as well as the clear differentiation between plant species in each cluster, and give a unique character to each space.
▼项目鸟瞰示意图
▼单元节点
设计单位:MDRDV
地点:韩国首尔
项目周期:2015 - 2017
规模:938m2公共道路和基础设施改造
Architects: MDRDV
Location : Seoul, South Korea
Year : 2015-2017
Size : 938m2 public path and infrastructure transformation
更新日期:2019-11-12 19:45:39
非常感谢 MDRDV 带来的精彩项目, 查阅更多Appreciations towards MDRDV for sharing wonderful work on hhlloo. Click to see more works!